Ratelade J, Klug NR, Lombardi D, Angelim MKSC, Dabertrand F, Domenga-Denier V, Al-Shahi Salman R, Smith C, Gerbeau JF, Nelson MT, Joutel A. Reducing Hypermuscularization of the Transitional Segment between Arterioles and Capillaries Protects Against Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Circulation. 2020 Mar 18;. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.040963. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 32183562. Download from HAL-INSERM
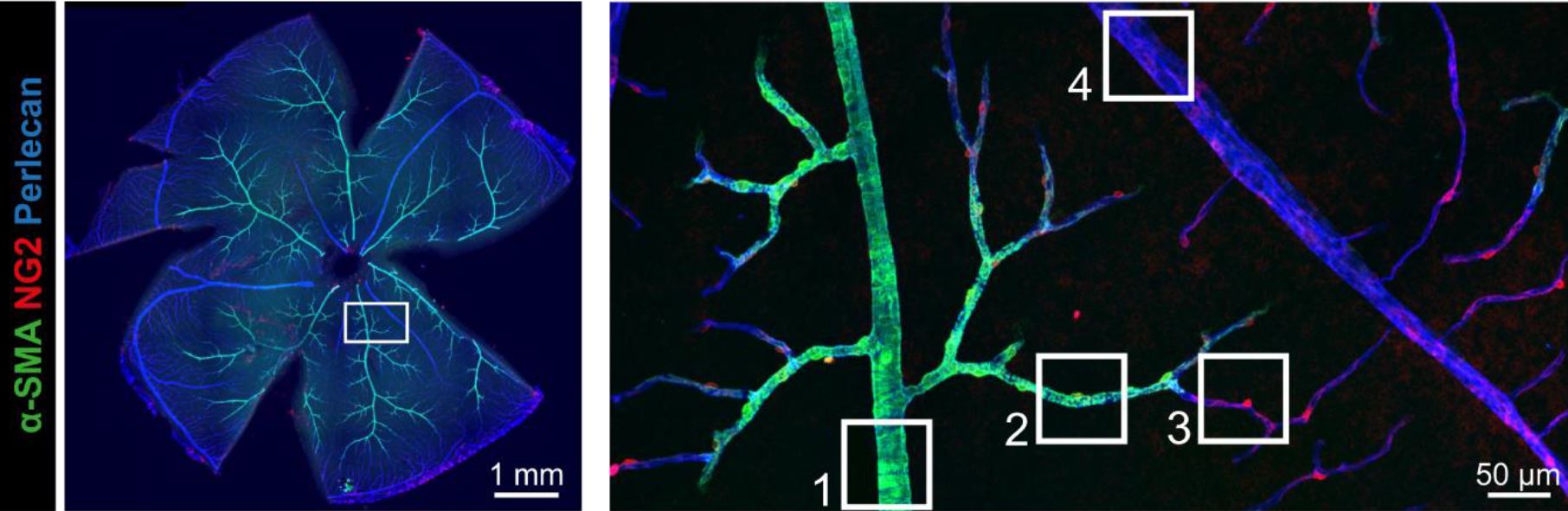
Background: Spontaneous deep intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a devastating subtype of stroke without specific treatments. It has been thought that smooth muscle cell (SMC) degeneration at the site of arteriolar wall rupture may be sufficient to cause hemorrhage. However, deep ICHs are rare in some aggressive small vessel diseases that are characterized by significant arteriolar SMC degeneration. Here we hypothesized that a second cellular defect may be required for the occurrence of ICH. Methods: We studied a genetic model of spontaneous deep ICH using Col4a1+/G498V and Col4a1+/G1064D mouse lines that are mutated for the alpha1 chain of Collagen type IV. We analyzed cerebroretinal microvessels, performed genetic rescue experiments, vascular reactivity analysis and computational modeling. We examined post-mortem brain tissues from patients with sporadic deep ICH. Results: We identified in the normal cerebroretinal vasculature a novel segment between arterioles and capillaries, herein called the transitional segment (TS), that is covered by mural cells distinct from SMCs and pericytes. In Col4a1 mutant mice, this TS was hypermuscularized, with a hyperplasia of mural cells expressing more contractile proteins, whereas the upstream arteriole exhibited a loss of SMCs. Mechanistically, TS showed a transient increase in proliferation of mural cells during post-natal maturation. Mutant brain microvessels, unlike mutant arteries, displayed a significant upregulation of SM genes and Notch3 target genes, and genetic reduction of Notch3 in Col4a1+/G498V mice protected against ICH. Retina analysis showed that hypermuscularization of the TS was attenuated but arteriolar SMC loss unchanged in Col4a1+/G498V, Notch3+/- mice. Moreover, hypermuscularization of the retinal TS increased its contractility and tone and raised the intravascular pressure in the upstream feeding arteriole. We similarly found hypermuscularization of the TS and focal arteriolar SMC loss in brain tissues from patients with sporadic deep ICH. Conclusions: Our results suggest that hypermuscularization of the TS, via increased Notch3 activity, is involved in the occurrence of ICH in Col4a1 mutant mice, by raising the intravascular pressure in the upstream feeding arteriole and promoting its rupture at the site of SMC loss. Our human data indicate that these 2 mutually reinforcing vascular defects may represent a general mechanism of deep ICH.
Keywords: Hypermuscularization; Notch3; collagen IV; transitional segment.
This part of the website could either be in French or English, depending on the sources of the actualities.