Deficient LEF1 expression is associated with lithium resistance and hyperexcitability in neurons derived from bipolar disorder patients. Santos R, Linker SB, Stern S, Mendes AP, Shokhirev MN, Erikson G, Randolph-Moore L, Racha V, Yeni K, Kelsoe JR, Bang AG, Alda M, Marchetto MC, Gage FH. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-00981-3. Download from HAL-INSERM
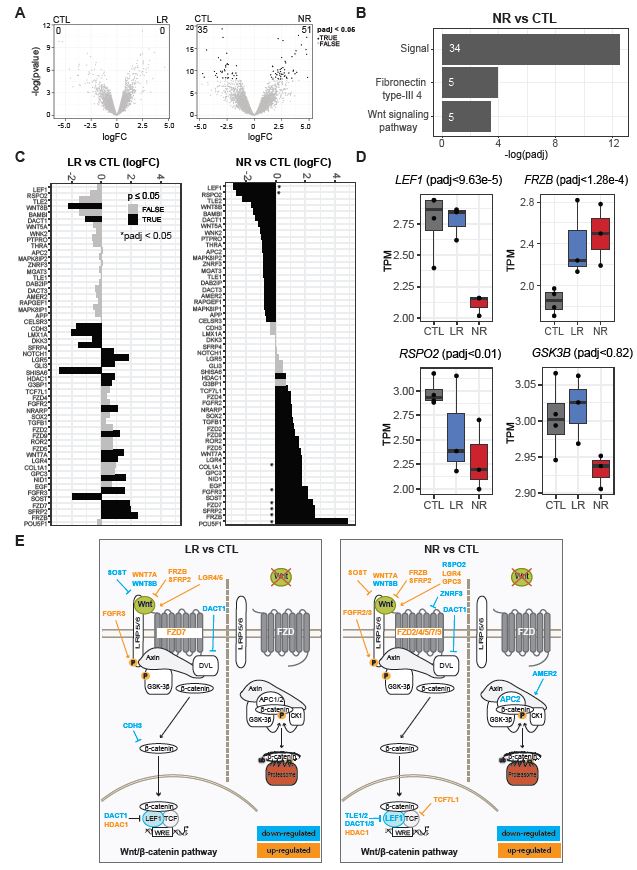
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a psychiatric condition characterized by depressive and manic episodes that affect 2% of the world population. The first-line long-term treatment for mood stabilization is lithium (Li). Induced pluripotent stem cell modeling of BD using hippocampal dentate gyrus-like neurons derived from Li-responsive (LR) and Li-non-responsive (NR) patients previously showed neuronal hyperexcitability. Li treatment reversed hyperexcitability only on the LR neurons. In this study we searched for specific targets of Li resistance in NR neurons and found that the activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was severely affected, with a significant decrease in expression of LEF1. Li targets the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by inhibiting GSK-3β and releasing β-catenin that forms a nuclear complex with TCF/LEF1, activating the Wnt/β-catenin transcription program. Therefore, we propose that downregulation of LEF1 may account for Li resistance in NR neurons. Our results show that valproic acid (VPA), a drug used to treat NR patients that also acts downstream of GSK-3β, upregulated LEF1 and Wnt/β-catenin gene targets, increased transcriptional activity of complex β-catenin/TCF/LEF1, and reduced excitability in NR neurons. In addition, decreasing LEF1 expression in control neurons using shLEF1 caused hyperexcitability, confirming that the impact of VPA on excitability in NR neurons was connected to changes in LEF1 and in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Our results suggest that LEF1 may be a useful target for the discovery of new drugs for BD treatment.
This part of the website could either be in French or English, depending on the sources of the actualities.